The pilot MAR scheme in Recife, Pernambuco, Brazil (BRA2) is currently implemented. An ASR well will infiltrate pre-treated rainwater harvested from a roof into the confined coastal aquifer to reduce the effects of flood events in the urban district as well as saltwater intrusion.
The study area is located in the Metropolitan Region of Recife (RMR), on the north-eastern coast of Brazil. The pilot-scale scheme is situated at a public school in the Pina neighborhood, one of the most densely populated areas of Recife. The school is located about 340 meters from the sea.
Recent droughts (1998-1999, 2012-2016) and rising water demand over the last three decades due to a steady population growth have led to overexploitation of groundwater resources, degradation of water quality, as well as potential subsidence. At the same time, the RMR is exposed to frequent extreme rain events and surface runoff causing urban floods.
The implementation of the ASR pilot-scale scheme aims to mitigate the flooding problem, to protect and restore groundwater resources and prevent saline intrusion. The pilot scheme furthermore intends to provide the basis to foster the upscaling and implementation of the system at larger scale. Figure 1 shows the school area where the ASR is being installed.

The pilot system consists of a harvesting water system, a pre-treatment stage, a water tank and a well (Figure 2).
Rainwater will be collected on the school roof and as a second step will be pre-treated by a sand filter. After removing the fine particles, the rainwater will be stored in a reservoir. The pre-treated rainwater will be infiltrated by gravity in the ASR well into the confined Upper Cabo aquifer. The ASR well is a multilevel well. Rainwater will be injected into one tube and can be later recovered from another tube. The tubes contain filter zones at 133-141 m and 166-170 m. Both tubes are 2 inches in diameter and made from PVC.
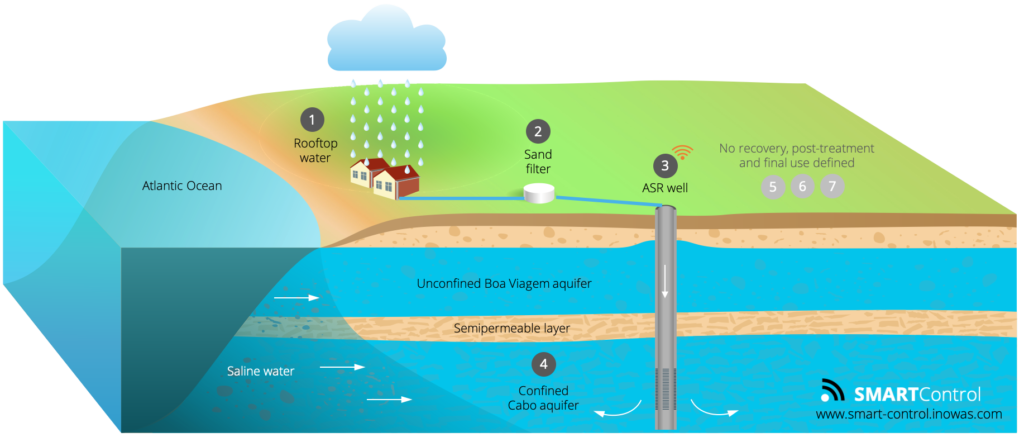
The MAR components of the Recife system are summarized below:
- Capture zone: Rooftop rainwater
- Pre-treatment: Sand filtration
- Recharge: ASR well
- Subsurface: Lower Cabo aquifer, sands
- Recovery: ASR well
- Post-treatment: not defined
- End use: not defined
Within SMART-Control, a real-time monitoring system will be installed to continuously monitor electrical conductivity and groundwater levels to evaluate the influence of the effect of the tide on the hydraulic load variation and to develop a sustainable groundwater management concept.